Deformability of soil



The Hollow Test and the True Triaxial Test
The Standard Penetration Tests
The Standard Penetration Tests aims to determine the SPT N value, which gives an indication of the soil stiffness and can be empirically related to many engineering properties.

Procedure
The test uses a thick-walled sample tube, with an outside diameter of 50mm and an inside diameter of 35mm, and a length of around 650mm. This is driven into the ground at the bottom of a borehole by blows from a slide hammer with a weight of 63.5kg (140 lb) falling through a distance of 760mm (30in). The sample tube is driven 150mm into the ground and then the number of blows needed for the tube to penetrate each 150mm (6in) up to a depth of 450mm (18in) is recorded. The sum of the number of blows required for the second and third 6 in. of penetration is termed the "standard penetration resistance," or the "N-value". In cases where 50 blows are insufficient to advance it through a 150mm (6in) interval the penetration after 50 blows is recorded. The blow count provides an indication of the density of the ground, and it is used in many empirical geotechnical engineering formulae.

The test is conducted inside a borehole. A 'split spoon' sampler is attached to the bottom of a core barrel and lowered into position at the bottom of the borehole. The sampler is driven into the ground by a drop hammer weighing 68 kg falling through a height of 76 cm. The number of hammer blows is counted. The number required to drive the sampler three successive 150mm increments is recorded. The first increment (0-150mm) is not included in the N value as it is assumed that the top of the test area has been disturbed by the drilling process. The SPT N is the number of blows required to achieve penetration from 150-450mm.
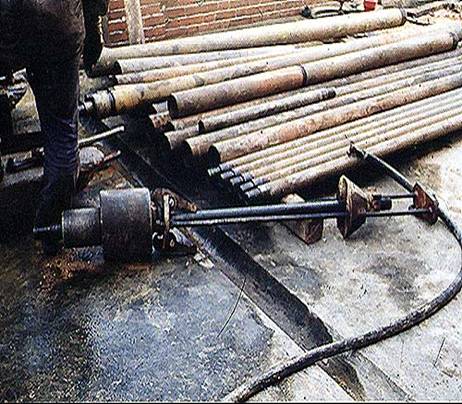

The hammer weight, drop height, spoon diameter, rope diameter etc. are standard dimensions.
After the test, the sample remaining inside the split spoon is preserved in an airtight container for inspection and description.