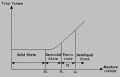
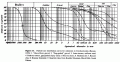
Granulometric structure of soil
| HOME | LITTERATURE | CONTACT US |
| Nature of soil |
| Structure or microstructure of soil |
| identification and classification of soil |
| Granulometric structure of soil |
| Phase relations and phisical state indexes of soil |
|
Granulometric structure of soil is defined by curve which is describing contents of grains different sizes expressed in percent. This kind of drawing is used in many countries. This diagram is participated in MIT (USA). Classification system like this is very simple for defining(definisanje) granicnih fractions of grains (gravel, clay, sand) and their relative sizes (big, small, large). The only two numbers are used and they are two and six. Experiment of spreading is used for classification large grain soil. While for classification small grain soil is used experiment which we know as hydrometric. Besides the shape of the granulometric curve, we can also use numerical index for describing large grain soil:
Consistency state limits or Atteberg s limits of consistency or we frequently use term – limit of plasticity. These limits are used exclusive for small grain soil. Atteberg s limits are used to define features of clay component in soil. The most important characteristic of clay material is that these materials change their consistency state in the dependence of water contents. Granica tecenja LL is defining by standard experiment in Kasagrande s apparatus. Granica plasticnosti (limit of placticity) PL is also defining by experiments. We could mention some notions which are very important for classification and they are index of consistency, flow index (LI), limit of assembling. UNIQUE CLASSIFICATION In nature we find different sorts of soil. In civil engineering the most appropriate is Unique classification. This classification system is based on suggestion who gave Casagrande (1948). That kind of classification is known as AC classification (Airfield Classification). In some countries a different kinds are used but the basic principle is the same everywhere. The basic principle: every type of soil can be described with two letters, two signs, or two symbols. Large grain soil is classified with size of grains by granulometric curve. The most important coefficient of uniform (Cu), and coefficient of estranged (Cz). Small grain soil which contains over 50 % of grains less than 0.075 mm is classified application granulometric composition. AC system is very useful sort for classification every type of soil in many applications like are building of roads, highways, airports, dams, foundations. In practice every type of classification type of soil, we can write down typical features which can be very useful in building process or drafting. |